The modern business landscape is undergoing a fundamental transformation. One of the most impactful shifts in recent years is the rise of decentralized innovation teams. These teams are reshaping how companies ideate, develop, and deploy new products or services. Instead of relying on centralized R&D departments or traditional hierarchies, organizations are now embracing distributed, agile, and autonomous innovation units that span geographies, time zones, and cultural boundaries.
Fueled by cloud-based collaboration tools, remote work trends, and a demand for faster and more adaptive innovation, decentralized teams have emerged as a key strategy for future-ready enterprises.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the concept, structure, benefits, challenges, technologies, and future of decentralized innovation teams—and how your business can harness their potential.
What Are Decentralized Innovation Teams?
A decentralized innovation team is a group of professionals working collaboratively across different locations, often independently from a single central authority, to create, test, and implement innovative ideas. These teams are often:
Geographically distributed
Cross-functional
Digitally connected
Autonomous or semi-autonomous
Outcome-driven
Unlike centralized teams that follow a top-down innovation model, decentralized teams empower individual units or employees to contribute ideas, drive projects, and make decisions without waiting for corporate approval.
Why Are Decentralized Teams on the Rise?
Several macroeconomic, cultural, and technological factors have accelerated the rise of decentralized innovation structures:
A. Remote Work Acceleration
The COVID-19 pandemic forced businesses to adopt remote work almost overnight. As companies adapted, they discovered the potential of distributed teams to deliver results without being physically co-located.
B. Digital Collaboration Tools
Platforms like Slack, Notion, Microsoft Teams, and Miro have enabled seamless communication, documentation, and brainstorming across time zones.
C. Global Talent Access
Hiring decentralized teams allows companies to tap into talent pools beyond their headquarters—enabling more diverse, inclusive, and specialized innovation.
D. Agile Product Development
Decentralized teams often operate using agile methodologies, which prioritize iteration, customer feedback, and rapid deployment—key to competitive innovation.
E. Startup Mentality in Enterprises
Large corporations are adopting startup-style innovation labs and remote squads to maintain relevance and compete with disruptive startups.
Key Characteristics of Decentralized Innovation Teams
To function effectively, decentralized teams share several common traits:
A. Autonomy
Each unit or team has the authority to make decisions, experiment, and implement solutions without excessive bureaucracy.
B. Accountability
Despite their independence, decentralized teams are held responsible for outcomes, results, and KPIs.
C. Diversity
Multicultural and multidisciplinary teams bring varied perspectives, fueling creativity and resilience.
D. Transparency
Open communication, clear goals, and shared platforms ensure everyone remains aligned and informed.
E. Flexibility
These teams are highly adaptive to market changes, customer feedback, and technological disruption.
Technologies Powering Decentralized Innovation
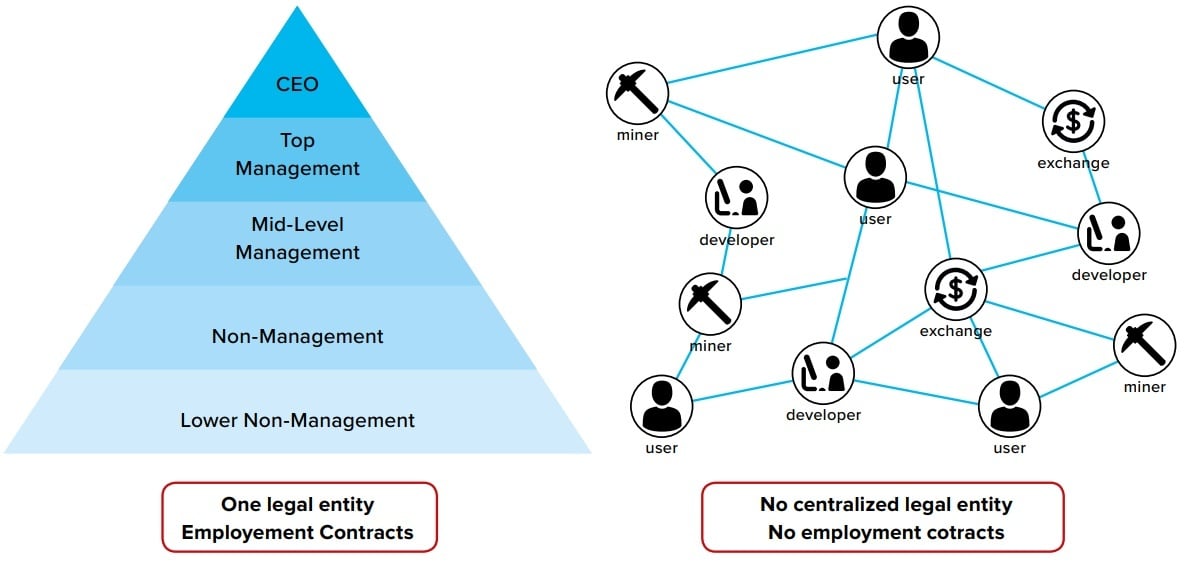
Technology plays a foundational role in enabling distributed innovation. Essential tools and systems include:
A. Project Management Platforms
Tools like Jira, Trello, and Asana help teams stay on track with sprints, tasks, and priorities.
B. Communication Tools
Slack, Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams allow real-time and asynchronous communication.
C. Document Collaboration
Cloud-based tools like Notion, Confluence, and Google Workspace allow teams to co-create and manage documentation effortlessly.
D. Version Control Systems
GitHub and GitLab allow collaborative development, testing, and deployment of software or product features.
E. Digital Whiteboards
Miro, Figma, and Lucidspark enable ideation, wireframing, and collaborative brainstorming across screens.
F. Innovation Management Software
Platforms like IdeaScale, Spigit, or Brightidea streamline crowdsourcing, evaluation, and incubation of new ideas.
Benefits of Decentralized Innovation Teams
Adopting decentralized structures offers several compelling advantages:
A. Faster Time to Market
Agile and autonomous units can develop and release new ideas without the delays associated with hierarchical approvals.
B. Greater Innovation Diversity
Diverse teams generate a wider range of creative solutions and are better equipped to serve global markets.
C. Increased Employee Engagement
Empowering employees at all levels fosters ownership, motivation, and job satisfaction.
D. Scalability
Decentralized models can scale innovation across departments, countries, and business units without overloading a central hub.
E. Risk Mitigation
Innovation efforts spread across teams reduce the risk associated with failed experiments or market misalignment.
Use Cases: Real-World Examples
Several companies have successfully embraced decentralized innovation:
A. GitLab
An all-remote company with over 2,000 employees across 60+ countries. GitLab’s success lies in its transparent documentation culture and decentralized approach to product development.
B. Amazon
Uses “two-pizza teams”—small, autonomous groups that work independently on new services or products.
C. Spotify
Adopts a “squad” model where cross-functional teams own specific parts of the product or platform.
D. Unilever
Launched a decentralized global innovation lab network to co-create with local teams and communities.
E. IBM
Uses internal innovation contests to crowdsource ideas from across their global workforce.
Challenges of Decentralized Innovation Teams

While decentralized teams offer clear advantages, they are not without challenges:
A. Communication Gaps
Without clear protocols, distributed teams may suffer from misalignment or information silos.
B. Cultural Differences
Time zone gaps, language barriers, and varying communication styles can hinder collaboration.
C. Technology Fragmentation
Inconsistent tool usage across teams can reduce productivity and hinder integration.
D. Decision-Making Confusion
Lack of clear ownership can lead to indecision or duplicated efforts.
E. Data Security
Collaborating across borders introduces cybersecurity and compliance challenges.
Best Practices for Managing Decentralized Innovation Teams
To unlock the full potential of decentralized innovation, organizations should follow these practices:
A. Establish Clear Governance
Define roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority early.
B. Invest in Unified Tools
Adopt standardized tools across teams for communication, documentation, and project tracking.
C. Embrace Asynchronous Work
Reduce dependency on real-time meetings; prioritize written updates, dashboards, and video recordings.
D. Promote Cross-Cultural Training
Foster understanding and empathy through cultural onboarding and communication workshops.
E. Encourage Psychological Safety
Create a culture where team members feel safe to speak up, experiment, and fail.
F. Align on Shared Goals
Ensure all teams are working toward a common mission, even if execution paths differ.
The Future of Decentralized Innovation
As AI, blockchain, and metaverse technologies evolve, decentralized innovation teams will become even more autonomous, data-driven, and creative. Key trends to watch include:
A. DAO-Driven Innovation
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) use blockchain to enable leaderless innovation ecosystems with token-based governance.
B. AI-Enhanced Collaboration
AI-powered co-pilots will streamline brainstorming, content creation, and product prototyping.
C. Innovation Marketplaces
Companies will open their APIs, data, or services to external innovators, creating digital marketplaces for co-creation.
D. Real-Time Global Hackathons
Virtual innovation events will connect creators worldwide, crowdsourcing new ideas on demand.
E. Employee-Driven Innovation Portals
Platforms where any employee can submit, pitch, and execute ideas using internal funding and decentralized support.
How to Get Started With Decentralized Innovation
For companies looking to implement decentralized innovation teams, the journey begins with intentional design and cultural alignment.
Step 1: Identify Innovation Priorities
Determine which products, markets, or challenges require agile experimentation.
Step 2: Assemble Cross-Functional Teams
Mix engineers, marketers, designers, and domain experts to build diverse squads.
Step 3: Define Metrics
Use OKRs (Objectives & Key Results) to align innovation teams with broader company goals.
Step 4: Launch a Pilot Program
Start with one or two decentralized teams before scaling across departments.
Step 5: Gather Feedback and Iterate
Use surveys, retrospectives, and performance metrics to refine your decentralized model.
Conclusion: Decentralization Is the New Innovation Model
Innovation is no longer confined to ivory towers or central R&D departments. In a world where speed, diversity, and adaptability determine market leadership, decentralized innovation teams are emerging as the superior model for future-ready organizations.
By leveraging digital tools, empowering employees, and fostering a culture of experimentation, businesses can unlock new levels of creativity and responsiveness. The question is no longer if decentralization works—it’s how quickly you can implement it.
Whether you’re a startup scaling quickly or an enterprise navigating disruption, building decentralized innovation teams may be the smartest investment you make this decade.